|
The process flow of die casting
(2018/11/7) In die casting production, die casting machines, die casting alloys and die casting are three major factors. The die casting process is a process in which the three elements are combined and used. Make various process parameters meet the needs of die casting production. The choice of injection specific pressure should be determined according to the structural characteristics of different alloys and castings. For the selection of filling speed, generally for castings with high thick wall or internal quality requirements, lower filling speed and high supercharging pressure should be selected; for castings with high wall thickness or surface quality and complex castings, should be selected Higher ratio and higher filling speed. 1. Pouring temperature The pouring temperature refers to the average temperature of the liquid metal from the time of pressing into the cavity. Since the temperature measurement of the liquid metal in the pressure chamber is inconvenient, it is generally expressed by the temperature in the holding furnace. The pouring temperature is too high, the shrinkage is large, the casting is prone to cracks, the grain size is large, and the sticking type can be caused; the pouring temperature is too low, and the defects such as cold partition, surface pattern and insufficient pouring are easily generated. Therefore, the pouring temperature should be considered simultaneously with the pressure, the die casting temperature and the filling speed. 2. Die casting temperature The cast type should be preheated to a certain temperature before use, generally using gas, blowtorch, electric appliance or induction heating. In continuous production, the temperature of die-casting tends to increase, especially for die-casting high-melting alloys, which rises rapidly. Excessively high temperatures, in addition to making the liquid metal sticky, the castings cool slowly, making the grains coarse. Therefore, when the temperature of the die-casting type is too high, cooling measures should be taken. It is usually cooled with compressed air, water or chemical media. 3. Filling and holding pressure Filling, holding and opening time 1) Filling time The time required for the liquid metal to enter the cavity to fill the cavity is called the filling time. The length of filling time depends on the size and complexity of the casting volume. For large and simple castings, the filling time is relatively long and the filling time for complex and thin-walled castings is shorter. The filling time is closely related to the cross-sectional area of the gate or the width and thickness of the gate, and must be correctly determined. 2) Holding pressure and opening time When the liquid metal filling cavity is completely solidified, the duration of the injection under the action of the injection punch is called the holding time. The length of the holding time depends on the material and wall thickness of the casting. After holding the pressure, the casting should be taken out. The time from the end of the injection to the opening of the die casting is called the opening time, and the opening time should be controlled accurately. The opening time is too short. Due to the low strength of the alloy, it may cause deformation when the casting is ejected and the self-pressing mold falls. However, if the opening time is too long, the casting temperature is too low, the shrinkage is large, and the core is drawn and the casting is ejected. The resistance is also big. Generally, the opening time is calculated according to the wall thickness of the casting 1 mm, and then it is adjusted for 3 seconds. 4. Die casting coating In the die-casting process, in order to avoid the welding of the casting and the die-casting type, the frictional resistance of the casting is reduced, and the coating is prevented from being excessively heated by the die-casting type. Requirements for coatings: 1) Good lubricity at high temperatures; 2) The volatile point is low, and the diluent can be quickly evaporated at 100-150 ° C; 3) No corrosion to die-casting and die-casting parts; 4) Stable performance In the air, the thinner should not volatilize excessively and thicken; 5) No harmful gases will be precipitated at high temperatures; 6) No fouling will occur on the surface of the die-cast cavity. 5. Casting cleaning The cleaning of castings is a very heavy task, and the workload is often 10 to 15 times the amount of die casting work. Therefore, with the increase of the productivity of the die casting machine and the increase of the output, it is very important to realize the mechanization and automation of the casting cleaning work. 1) Cut the gate and flash The equipment used for cutting gates and flashing is mainly punching machines, hydraulic presses and friction presses. Under a large number of production parts, special molds can be designed according to the structure and shape of the castings, and the cleaning tasks can be completed once on the punching machine. 2) Surface cleaning and polishing The surface cleaning is mostly performed by a common multi-angle roller and a vibration embedded cleaning device. For small and small parts that are not large in size, the multi-angle cleaning roller can be used, and the decorative parts with high surface requirements can be polished by cloth or leather polishing wheel. For the mass production of castings, a screw-type vibration cleaner can be used. The cleaned castings can also be surface treated and impregnated according to the requirements of use to increase gloss, prevent corrosion and improve air tightness. 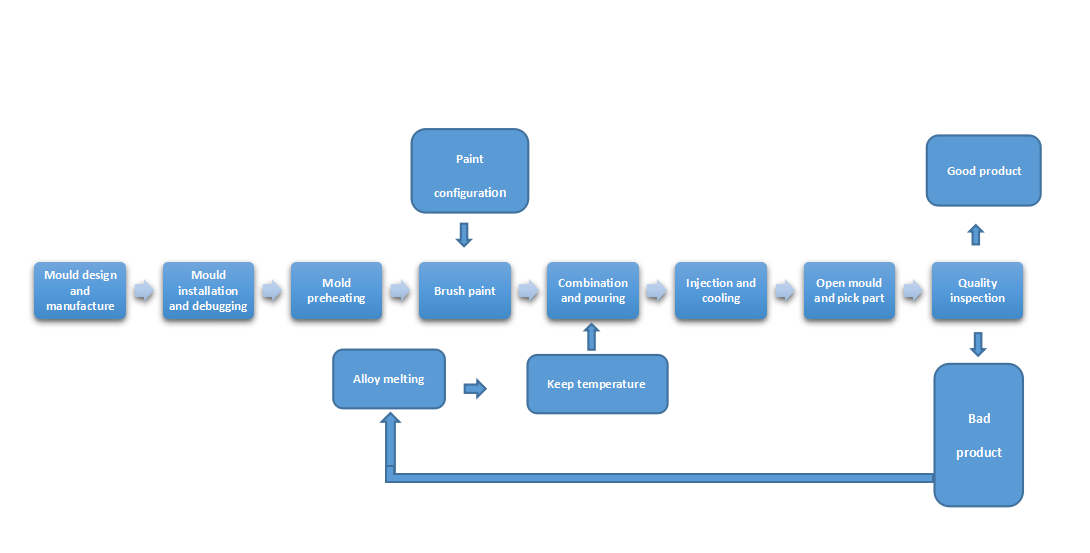 |
